Sail Design Process
 The ability of sail designers to create efficient aerofoils has improved beyond all recognition over the last 20 years mainly due to the advent of ever more powerful computer processors and design software along with the development of sail materials and manufacturing techniques.
The ability of sail designers to create efficient aerofoils has improved beyond all recognition over the last 20 years mainly due to the advent of ever more powerful computer processors and design software along with the development of sail materials and manufacturing techniques.
Ultimate Sails design software is a fully integrated suite of programmes that give our designers unlimited flexibility of boat, rig and sail analysis. We can test every element of the boat, rig and sails in a variety of conditions “on the screen” before manufacture. This combined with the ability to accurately compare finished results after sailing has reduced development time and costs significantly. With modern materials, sails can be designed with extreme accuracy to tight tolerances. We can produce sails for very specific uses whether its grand prix racing, off shore racing or performance cruising. Using the latest software technology, sails are designed and built to create the most efficient aerofoils giving back total control to the sailors on the water.
Here is an example of the design process from start to sailing:
Boat and rig: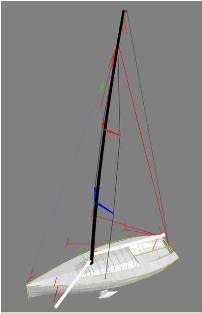
We start with either the sail plan or accurate measurements taken from an existing boat to create a 3D model of the boat and rig. We take into account the size of the boat, its displacement, righting moment, yaw and designers VPPs. On the rig we specify sheeting angles, spreader angles, track positions, mast properties including surface area, rake, initial mast bend, maximum mast bend and mast twist. We can also take into account the mechanical properties of the rig’s structure and allow for stretch of head stay, shrouds, halyards and mast tip fade.
This drawing shows a hull and rig ready to accept sails with sheeting positions and halyards for a mainsail, Code 2 Jib, Code 0, asymmetric spinnaker on a pole and a spinnaker staysail.
Sails: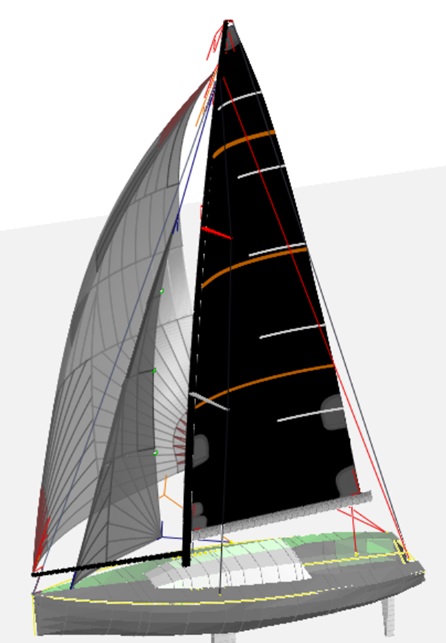
The next stage is to define the 3D surface of each sail and apply it to the rig. All sail dimensions are controlled in 3D and any type of sail can be placed on the rig including, mainsails, Genoas, Jibs, Code 0s, Asymmetrics, staysails etc.
Here you can see the 3D boat and rig with a mainsail, Code 0 on a spinnaker pole and Spinnaker Staysail set inbetween. The 3d modelling is so accurate that in this instance the actual sheeting position of the clews and position of the pole were within 10mm of the design calculation.
Sail plan optimisation for yacht designers:
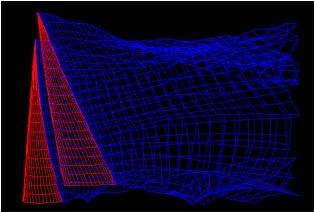 “Sailopt” is a revolutionary aerodynamic simulation software that computes the shapes and dimensions of sail designs. This software was developed at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology of Lausanne within a research program for the America’s Cup, where it has been extensively used for sail plan and sail design, and is now offered by Ultimate Sails as a service for yacht designers.
“Sailopt” is a revolutionary aerodynamic simulation software that computes the shapes and dimensions of sail designs. This software was developed at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology of Lausanne within a research program for the America’s Cup, where it has been extensively used for sail plan and sail design, and is now offered by Ultimate Sails as a service for yacht designers.
All upwind sails should function as efficient wings, developing the maximum lift with the minimum drag and heeling moment. This goal is achieved when the separation of the flow is minimized. These choices reflect the two main objectives of sail computations: the calculation of precise sail coefficients to feed the Velocity Prediction Program (VPP), and the determination of the optimum sail dimension and shape to aid the sailmaker in the design of the sails.
Optimisation of Upwind Sails
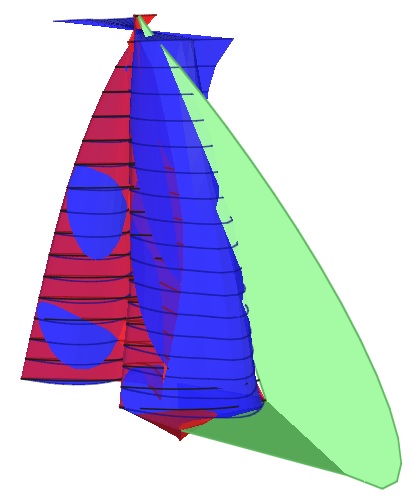
To determine the sail shape that maximizes the thrust for a given condition of wind speed and angle, an inverse 3D Vortex Lattice Method has been developed. With this approach several different constraints can be added very easily. Sails can be optimized with or without the constraint of maximum heeling moment. Limiting values of the sectional lift coefficient can be included to prevent stall. The viscous drag (taking into account the separation of the flow behind the mast) is added at each section using 2D drag coefficients that have been previously calculated using Fluent (a Navier-Stokes flow solver) for different combinations of camber ratio and mast dimension. During the iteration procedure unrealistic sail shapes can be discarded. Typical is the case of mainsails having an inverse camber in the upper part; theoretically this shape maximises the thrust in strong wind conditions, but is obviously very difficult to trim. Using this code it is possible to obtain the complete polar diagram of the “best” sails in upwind conditions and their corresponding shapes.
“Sailopt” also takes into account vertical wind shear and the water surface symmetry effect to output:
- Aerodynamic resulting forces and moments (driving force, heeling force, vertical force, heeling moment, yawing moment, pitching moment), all extremely useful for a boat designer to design and position the appendages, to feed the VPP with very precise upwind aerodynamic coefficients and to compare the performance of different possible sail plans.
- 3D optimum sail flying shape and sail trim, again very useful for the boat designer to help position the headsail tracks and the standing rigging, and for the sail designer to evaluate optimum camber and twist of each section of the upwind sails.










